Big data refers to extremely large and complex datasets that are beyond the capabilities of traditional data processing and management tools to handle efficiently. These datasets are characterized by their volume, velocity, variety, and, more recently, by their veracity and value. Let’s break down these characteristics:
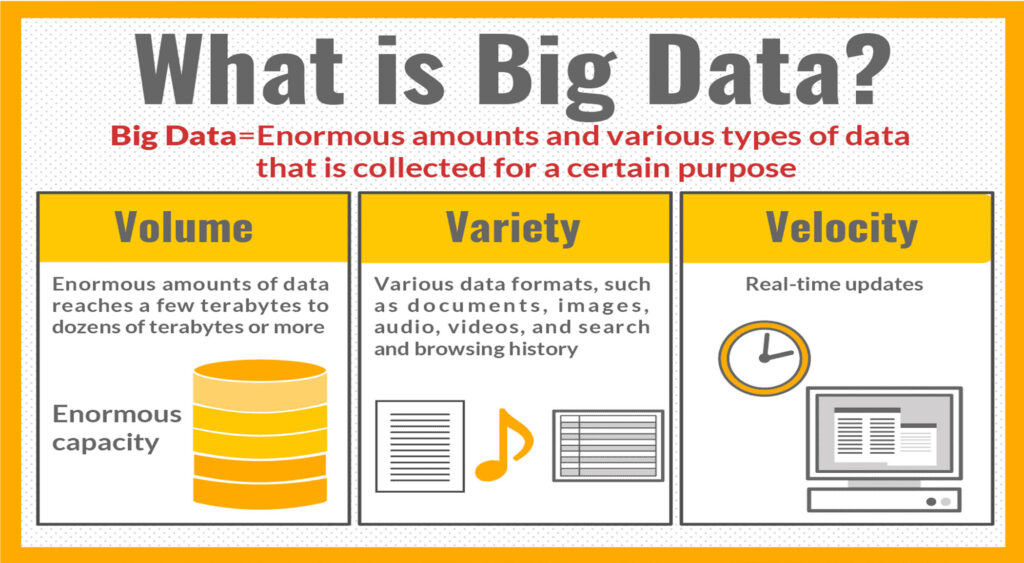
- Volume: Big data typically involves massive amounts of data. This can range from terabytes to petabytes and beyond. The volume of data is often too large to be processed by conventional databases and tools.
- Velocity: Data is generated and collected at an unprecedented speed. This data is often streaming in real-time from various sources such as social media, sensors, and online transactions. The ability to process and analyze data in real-time is a key aspect of big data.
- Variety: Big data comes in various formats and types. It includes structured data (like databases), semi-structured data (like XML files), and unstructured data (such as text documents, social media posts, and multimedia content). Big data solutions must be able to handle this diversity.
- Veracity: Veracity relates to the trustworthiness and reliability of the data. With so much data being generated, there’s a challenge in ensuring data quality and accuracy. Cleaning and validating data are essential steps in dealing with big data.
- Value: The ultimate goal of working with big data is to extract valuable insights, patterns, and knowledge from it. Businesses and organizations aim to make data-driven decisions, optimize operations, and gain a competitive edge.
To effectively work with big data, various technologies and techniques have emerged, including distributed computing frameworks (such as Hadoop and Spark), NoSQL databases, machine learning, and data mining algorithms. These tools help in storing, processing, and analyzing big data to derive meaningful information and business intelligence.
Big data is relevant in a wide range of fields, including business, healthcare, finance, social media, science, and government. It’s used for tasks like predictive analytics, fraud detection, recommendation systems, and scientific research. In essence, big data represents the potential for valuable insights hidden within massive and complex datasets, provided that the right tools and methodologies are applied to extract and leverage that information.