Microsoft launched Windows Vista on January 30, 2007. Windows Vista is the successor to Windows XP and represented a major release in the Windows operating system family. It introduced a range of new features, improvements, and changes to the Windows user interface and underlying architecture. Here are some key points about the launch of Windows Vista:
- Editions: Windows Vista is released in several editions, including Windows Vista Home Basic, Home Premium, Business, Enterprise, and Ultimate. Each edition offer different features and capabilities.
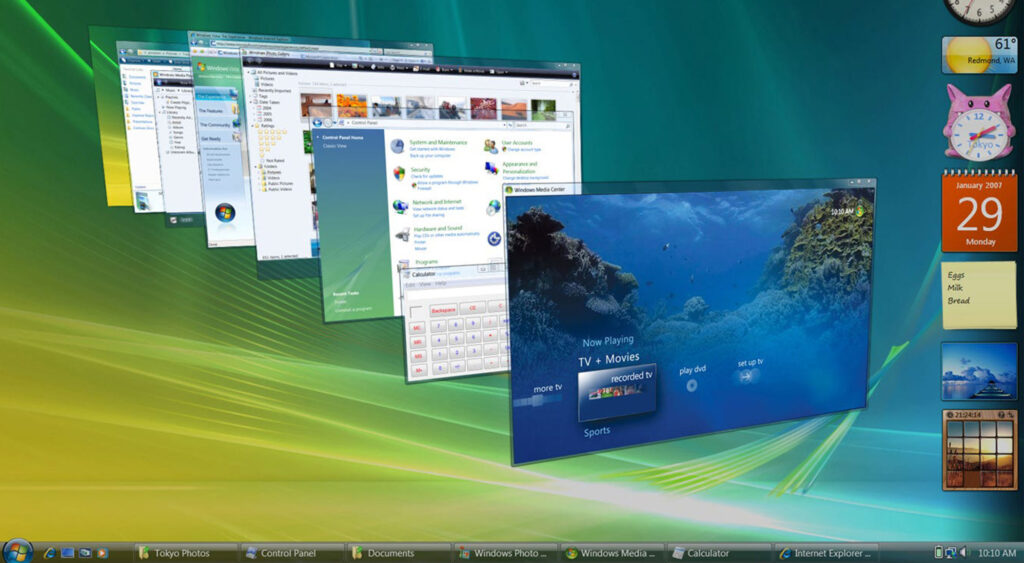
- User Interface: Windows Vista featured a significant overhaul of the user interface. It introduced the “Aero” theme, which included transparent window frames, visual effects, and improved window management.
- Search and Organization: The new Windows Search feature made it easier to find files and documents. Windows Vista also introduced the concept of Libraries to organize and manage files more effectively.
- Security Enhancements: Windows Vista including many security improvements, such as User Account Control (UAC), Windows Defender for malware protection, and enhancements to the Windows Firewall.
- Windows Aero: The Windows Aero interface including features like Flip 3D, which provided a 3D view of open windows, and live thumbnails in the taskbar, making it easier to manage and switch between open applications.
- Networking and Connectivity: Windows Vista including enhanced networking capabilities, improved support for wireless networking, and new features like Network Center to simplify network setup.
- Multimedia: Windows Vista feature Windows Media Player 11, which improved media playback and organization. It also introduced new multimedia formats and support for high-definition content.
- DirectX 10: Windows Vista is the first version of Windows to support DirectX 10, which brought significant improvements in graphics and gaming performance.
- Hardware Requirements: Windows Vista has higher hardware requirements compared to its predecessor, Windows XP, which meant that some older computers were not capable of running it effectively.
- Compatibility Issues: The launch of Windows Vista is accompanied by some compatibility issues with existing software and drivers, which caused initial adoption challenges for users and businesses.
- Edition Consolidation: In response to feedback and criticism, Microsoft streamlined the Windows Vista editions to make it less confusing for consumers and businesses.
- Service Packs: Microsoft planing to released service pack SP1 to address issues, improve performance, and enhance the overall stability of Windows Vista.
Windows Vista is met with a mixed reception. While it introduced several important features and security enhancements, it also facing criticism for its system requirements and early compatibility issues. Many users and organizations continued to use Windows XP.



